Turns any 2d texture into a 3d texture you can place on the surface using one of the available projection types. Use to adjust the texture placement on the surface.
Find this utility in the Create Bar (see Hide, resize or customize the Create bar).
To use this utility, see Use the Projection utility.
Displays the Projection manipulators in the scene view.
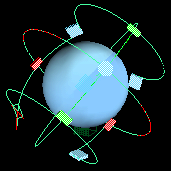
Using these manipulators in combination with Maya’s transform tools, you can orient and position the texture map in three dimensions. The manipulators for texture mapping are exactly the same as those used for texturing polygons. See the Polygon modeling overview in the Polygonal Modeling guide for details.
The texture map coincides with the bounding box of the mapped object or set. See also Interactive Placement.
Select a projection type from the drop-down list to display seven projection manipulators.
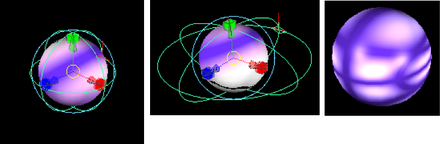
Places the texture inside a ball and projects it onto the object. For example, Maya projects the texture as if a candy wrapper is pulled around a lollipop. There is one pinch point to the mapping at the -z-pole, as opposed to the two pinch points at the +y and -y poles in spherical and cylindrical mapping.
You have a background sequence with a vase on a table you want to blow up. It can be difficult to produce a parametric or solid texture map that exactly matches the vase, but if you use the Perspective Proj Type, you can project the real image of the vase from the background sequence onto a 3D vase placed in a matching position. This allows a perfect match of textures from the camera’s point of view.
You want to place a 3D flying saucer within an image of a street scene. The image of the street scene should accurately reflect onto the flying saucer. You could do this with an environment texture, but that would require that you have other images available—if you use the Perspective Proj Type, you can project the image of the street scene onto stand-in geometry. The image projected onto the stand-in geometry accurately reflects onto the flying saucer.
Control a Projection node when the Proj Type is Perspective.
Controls how the texture fits to the camera when Proj Type is Perspective. Select from the following:
Controls the amount of fractal noise added to a Projection node. (Adding fractal noise randomizes or blurs the texture).
Controls the amount of calculation done by the texture when Ripples are added. Fractal noise such as ripples are created by a mathematical process; as the process goes over more levels, it produces a more detailed fractal, but takes longer. Normally, the texture chooses a level appropriate for the volume rendered. You can use Depth Min and Depth Max to control the minimum and maximum amount of calculation.
 Except where otherwise noted, this work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License
Except where otherwise noted, this work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License