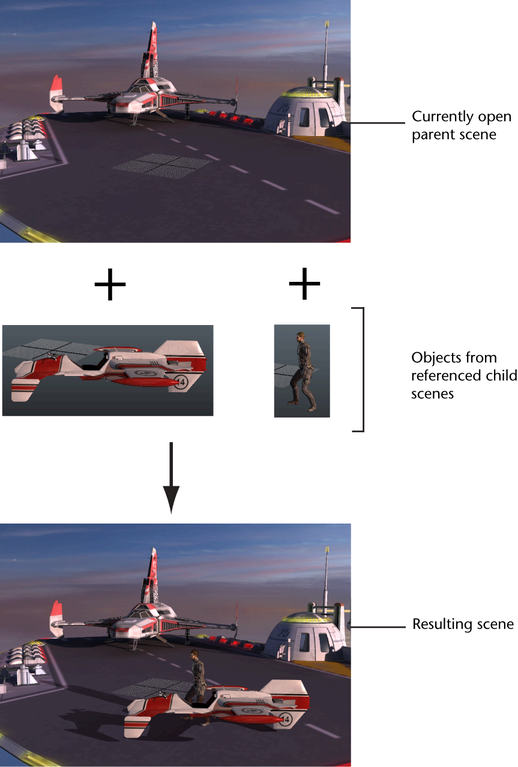
File referencing allows you to assemble multiple objects, such as modeled polygons, shading materials, and animated characters, without importing the files or objects into a scene. When you create a file reference, the contents of the referenced file appears in the scene, but the data for the objects is read or referenced from pre-existing files that remain separate and unopened. Using file referencing lets you use Maya objects and scenes in collaborative production situations where multiple users need to work concurrently and share various scene assets in complex scenes.
A scene file that references other files is known as a parent scene to indicate its position within the file referencing hierarchy. A parent scene reads or references other files called child scenes. Even though the referenced child scenes appear in the parent scene, the child scene data remain separate from the parent scene at all times.
A reference node is created for each child scene when it is referenced into a parent scene. The Outliner displays reference
nodes with an  icon and referenced objects with an
icon and referenced objects with an  icon. The reference node maintains the link between parent scene and child scene, so that when the parent scene is saved
and reopened, the references are retained in the parent scene. When a referenced object is modified in the parent scene, the
reference node stores these edits. See Reference edits.
icon. The reference node maintains the link between parent scene and child scene, so that when the parent scene is saved
and reopened, the references are retained in the parent scene. When a referenced object is modified in the parent scene, the
reference node stores these edits. See Reference edits.
 Except where otherwise noted, this work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License
Except where otherwise noted, this work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License