The following mental ray for Maya shaders are particularly useful and we recommend that you add them to your workflow.
The mia_material_x material shader can be used to simulate most architectural materials such as metal, wood and glass. This shader is recommended because it is versatile and produces HDR output. It provides an updated rendering algorithm as compared to older shaders such as the dielectric_material and dgs_material and has advanced features such as ambient occlusion. Many useful presets are available for this shader, for example: chrome, copper, frosted glass, physical glass, water, rubber and so forth.
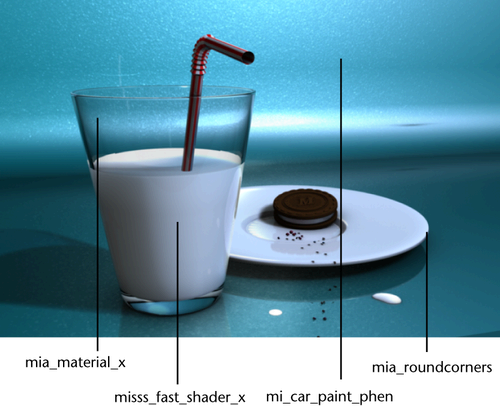
The mia_material_x shader was used to create the glass in the image above.
The misss_fast_shader_x shader can be used to simulate the effect of light bouncing between materials. Use this shader to simulate translucent surfaces such as skin and wax. This shader is recommended because it is a relatively fast way to render such an advanced lighting effect.
The misss_fast_shader_x was used to create the milk in the image above.
The mi_car_paint_phen shader simulates a tri-coat paint, with a base coat, flakes, and a gloss. This shader can be used to simulate cars as well as other types of models that require a metallic and glossy look, for example, cell phones.
The mi_car_paint_phen shader was used to create the background/countertop in the image above. You can see that it produces an iridescent look.
The mia_roundcorners shader allows you to save time and reduce geometry complexity because it obviates the need for you to model bevel edges. In addition, this shader is recommended because it works with all shaders, including Maya shaders. Simply map mia_roundcorners to the shader's bump attribute, but remember to perform your render using mental ray for Maya.
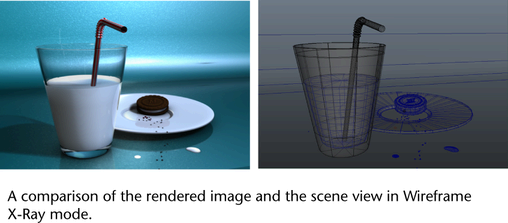
In the image above, mia_roundcorners was used to create the round edges of the plate. Compare the rendered image to that of the scene view in wireframe mode.