The Render Manager > mental ray (Global Renderer)
The Render Manager > (expand a pass) > mental ray
Set a current pass and choose Render > Render > Renderer Options from the Render toolbar.
Options: Color Control
Filtering Settings complement the antialiasing procedure in post-processing — ensuring even more antialiasing. Each of the five Filter Type settings (Gauss, Box, Triangle, Mitchell, and Lanczos) process subsamples — surrounding and including the pixel that is being rendered — using the height and width of the filter. Based on the value of the pixel, mental ray takes the average of every pixel and its surrounding pixels and removes aliasing artifacts.
When you adjust the Filtering settings, the Filter Size value for each filter type defines the size of the filter. Larger sizes make the image softer, smaller sizes make the image sharper.
The selected filter is applied as an algorithm defining a curve that peaks at the center of the sampled pixel.
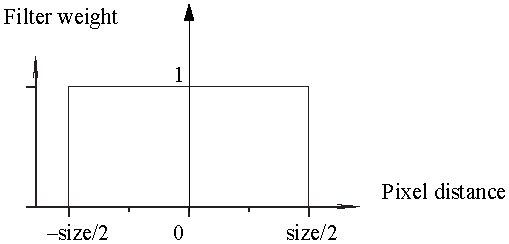
The Boxfilter sums up all the samples in the filter area with an equal weight. Box is the fastest filtering method. A good size for box filtering is 1.
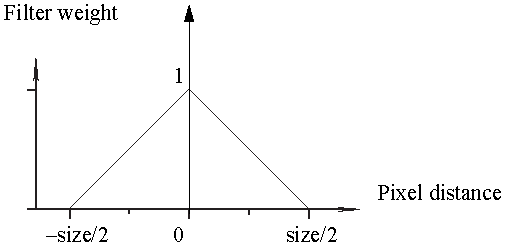
The Trianglefilter uses a linear curve that affects the pixels so that the least filtering happens at the edges of the sampled area. A good size for triangle filtering is 2.
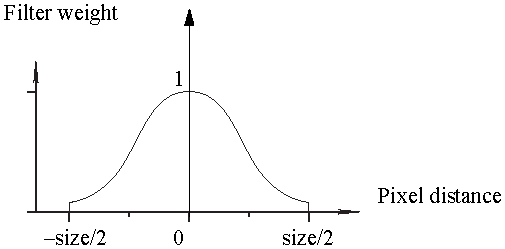
The Gaussfilter uses a sloped curve, weighting the sampling gently at the top of the peak and toward the edge of the sampled area. This filtering method is often used to control the soft staircase artifact effect. A good size for Gauss filtering is 3.
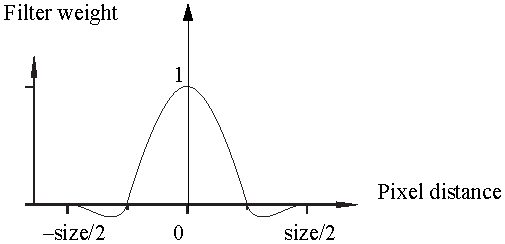
The Mitchellfilter uses a narrower bell-shaped curve than the Gaussian filter. The curve can go into negative values near the edges. A good size for Mitchell filtering is 4.
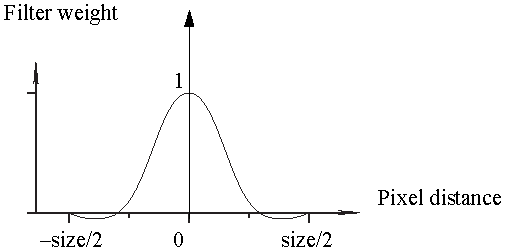
The Lanczosfilter uses a narrower, less bell-shaped curve than the Gaussian filter. The curve can go into negative values near the edges. A good size for Lanczos filtering is 4.
For more information, see Antialiasing, Sampling, and Filtering Tips & Tricks.
Activating the Jitter sub-pixel samples option randomizes the subsampling pattern, which prevents any potential artifacts from taking on a regular pattern. As a result, they are much more difficult for the naked eye to detect. This makes the antialiasing appear more natural and less interpolated.
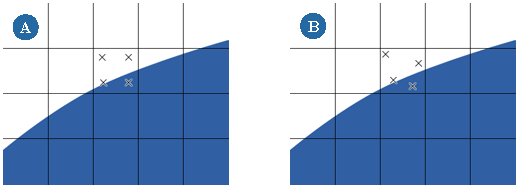
Shown above are two methods of sampling. Each sample is marked by an X. Image (A) is an example of default sampling. Some Jitter is added to the sampling (B). Notice how the sampling area is more random and the surface becomes smooth but less rounded.