
Use a reflection map when you want your materials to reflect something other than the environment background. Control brightness using the Reflection brightness slider (must be adjusted for each environment).
Reflection maps override all other reflections in Ray Tracing. This means that any objects with this material will reflect only the map in both Hardware and Ray Tracing modes, and any other objects will not be reflected. This can result in the material appearing less reflective in Ray Tracing mode.
A reflection map must be a panoramic image in the “vertical cross” format. The image file should have an aspect ratio of 3:4 and pixel dimensions that are a power of 2 (24 x 32, 384 x 512, etc.). The image can either be a regular image (JPG, PNG, BMP) or a High Dynamic Range image (HDR, EXR).

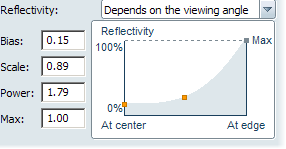
The mathematical function that relates the angle of view to the amount of reflection is called a "Fresnel function", and it is uses three parameters: Bias, Scale, and Power. The fourth parameter, Max, stops the amount of reflectivity from ever going above a certain number.
The formula is: reflectivity = bias + (scale * (1.0 - cos(view angle))**power)). You can try typing in these values directly, or use the reflectivity graph to change the Fresnel function. As you change the curve on the graph, the look of the material updates in the view.
Change the reflectivity by clicking and moving the handles. The left side of the graph shows how reflective the material is when viewed directly ("at center"). The right side shows you how reflective the material is when viewed on an oblique angle ("at edge").
Modulates or scales the intensity of the specular highlight. (This value is also called specular rolloff.) In other words, it affects how much of the highlight spreads into darker areas. Like highlight size, this value affects directional light, as configured with the Environment Light slider in the Directional Light and Shadows window.
