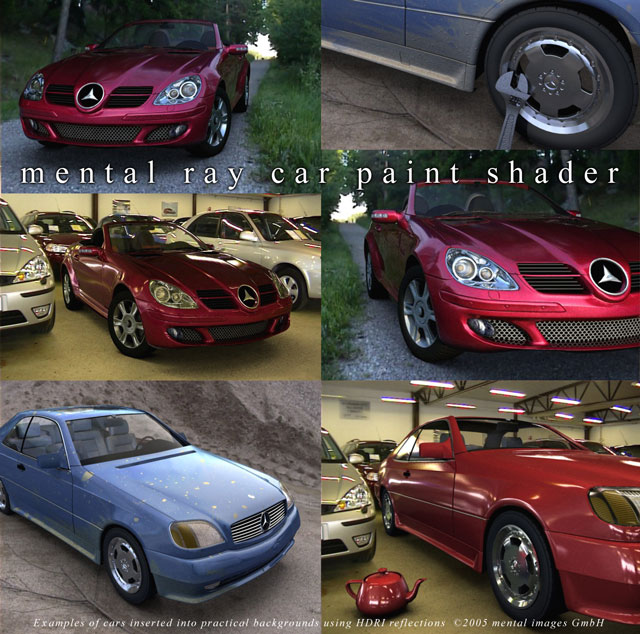

Example images rendered with mental ray car paint shader
Version 3.7.1.23
June 26 2008
The car paint related shaders are contained in the paint library.
The declaration of the shaders and phenomena are provided in the file
paint.mi. To use the shaders, the declaration file must be
included and the library linked:
link "paint.so"
$include "paint.mi"

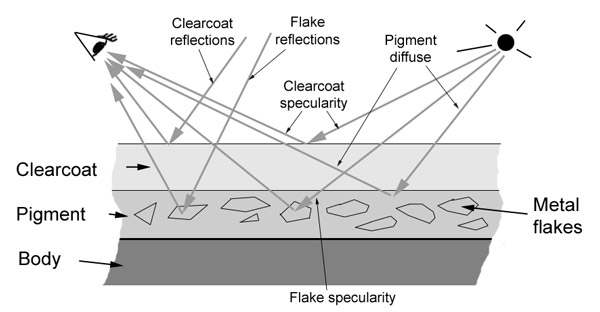
Car paint has several peculiar characteristics. On top of the cars bodywork is a thin layer of pigment. The properties of this layer is such that the actual perceived color shifts depending on the viewing angle as well as the incident angle of the incoming light.
Within this layer tiny metal flakes are suspended. The flakes reflect light and can be seen glittering on a sunny day, due to individual flakes reflecting sunlight directly at the observer.
On top of this is a clear-coat layer, which can be more or less reflective and more or less glossy, depending on the quality of the layer and any added wax coating. Most notably, this layer tends to exhibit a pronounced fresnel effect, reflecting more light at glancing angles.
The mi_car_paint_phen or mi_car_paint_phen_x should be applied as a surface shader in a material. The latter variant performs the same calculations but returns the individual components before compositing into the final color as separate channels. The phenomenon supports:
The phenomena have the following declarations:
declare phenomenon "mi_car_paint_phen" (
color "ambient",
color "base_color",
color "edge_color",
scalar "edge_color_bias",
color "lit_color",
scalar "lit_color_bias",
scalar "diffuse_weight",
scalar "diffuse_bias",
color "flake_color",
scalar "flake_weight",
scalar "flake_reflect",
scalar "flake_exp",
scalar "flake_density",
scalar "flake_decay",
scalar "flake_strength",
scalar "flake_scale",
color "spec",
scalar "spec_weight",
scalar "spec_exp",
color "spec_sec",
scalar "spec_sec_weight",
scalar "spec_sec_exp",
boolean "spec_glazing",
color "reflection_color",
scalar "edge_factor",
scalar "reflection_edge_weight",
scalar "reflection_base_weight",
integer "samples",
scalar "glossy_spread",
scalar "max_distance",
boolean "single_env_sample",
color "dirt_color",
scalar "dirt_weight",
scalar "irradiance_weight",
scalar "global_weight",
integer "mode",
array light "lights"
)
declare phenomenon
struct {
color "result", # main output
color "ambient_result",
color "ambient_raw",
color "ambient_level",
color "diffuse_result",
color "diffuse_raw",
color "diffuse_level",
color "indirect_result",
color "indirect_raw",
color "indirect_level",
color "spec1_result",
color "spec1_raw",
color "spec1_level",
color "spec2_result",
color "spec2_raw",
color "spec2_level",
color "flake_result",
color "flake_raw",
color "flake_level",
color "flake_refl_result",
color "flake_refl_raw",
color "flake_refl_level",
vector "flake_normal",
color "dirt_result",
color "dirt_raw",
color "dirt_level",
color "reflection_result",
color "reflection_raw",
color "reflection_level"
} "mi_car_paint_phen_x" (
color "ambient",
color "base_color",
color "edge_color",
scalar "edge_color_bias",
color "lit_color",
scalar "lit_color_bias",
scalar "diffuse_weight",
scalar "diffuse_bias",
color "flake_color",
scalar "flake_weight",
scalar "flake_reflect",
scalar "flake_exp",
scalar "flake_density",
scalar "flake_decay",
scalar "flake_strength",
scalar "flake_scale",
color "spec",
scalar "spec_weight",
scalar "spec_exp",
color "spec_sec",
scalar "spec_sec_weight",
scalar "spec_sec_exp",
boolean "spec_glazing",
color "reflection_color",
scalar "edge_factor",
scalar "reflection_edge_weight",
scalar "reflection_base_weight",
integer "samples",
scalar "glossy_spread",
scalar "max_distance",
boolean "single_env_sample",
color "dirt_color",
scalar "dirt_weight",
scalar "irradiance_weight",
scalar "global_weight",
integer "mode",
array light "lights"
)
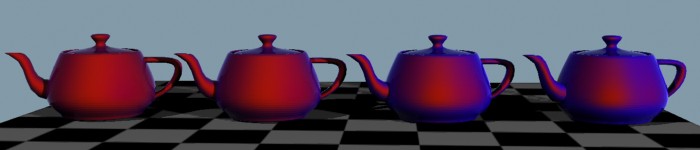
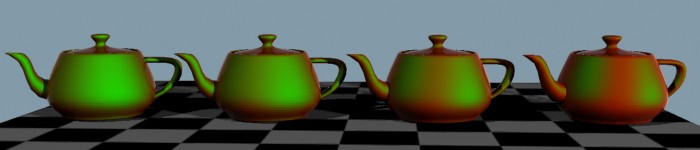



Clear-coat tends to reflect more at glancing angles (edges). Optionally, clear-coat layers may be glossy.
The glossy reflections are created with the help of the base shader mib_glossy_reflections and thus the parameters max_distance (limiting the reach of reflective rays) and single_env_sample (optimizing lookup of environment maps) are exposed parameters of the shader mib_glossy_reflection. Only a subset of the parameters are exposed, if more are required, one can either build a custom shading graph or create ones own variation of the mi_car_paint_phen Phenomenon.
A simple lambertian dirt layer covers the underlying paint and clear-coat layers.

This shader is used to facilitate the rendering of metallic paint. However, it only takes care of the pigmentation and the flakes, not the very important clear-coat reflections. To accomplish the full effect, it needs to be combined with a reflection shader (i.e. connecting it to the base_material parameter of mib_glossy_reflection). It also needs a bump shader for the flakes, like mi_bump_flakes).
For convenience, phenomena like mi_car_paint_phen are available which also support a dirt layer. Its documentation has slightly more detailed description of the parameters with example images.
The shader supports:
The shader comes in two variants, as mi_metallic_paint which returns a single final composited color, and mi_metallic_paint_x which additionally returns separate channels for the individual components before compositing.
declare shader
color "mi_metallic_paint" (
color "ambient" default 0 0 0 1,
color "base_color" default 0.8 0.1 0.0 1,
color "edge_color" default 0.0 0.0 0.0,
scalar "edge_color_bias" default 1.0,
color "lit_color" default 0.6 0.0 0.2,
scalar "lit_color_bias" default 8.0,
scalar "diffuse_weight" default 1.0,
scalar "diffuse_bias" default 1.5,
scalar "irradiance_weight" default 1.0,
color "spec" default 1 1 1 1,
scalar "spec_weight" default 0.2,
scalar "spec_exp" default 60.0,
color "spec_sec" default 1 1 1 1,
scalar "spec_sec_weight" default 0.3,
scalar "spec_sec_exp" default 25.0,
boolean "spec_glazing" default on,
color "flake_color" default 1.0 1.0 1.0 1,
scalar "flake_weight" default 1.0,
scalar "flake_reflect" default 0.0,
scalar "flake_exp" default 45.0,
scalar "flake_decay" default 0.0,
shader "flake_bump",
scalar "global_weight" default 1.0,
integer "mode" default 3,
array light "lights"
)
version 2
apply material
end declare
declare shader
struct {
color "result",
color "ambient_result",
color "ambient_raw",
color "ambient_level",
color "diffuse_result",
color "diffuse_raw",
color "diffuse_level",
color "indirect_result",
color "indirect_raw",
color "indirect_level",
color "spec1_result",
color "spec1_raw",
color "spec1_level",
color "spec2_result",
color "spec2_raw",
color "spec2_level",
color "flake_result",
color "flake_raw",
color "flake_level",
color "flake_refl_result",
color "flake_refl_raw",
color "flake_refl_level",
vector "flake_normal"
} "mi_metallic_paint_x" (
color "ambient" default 0 0 0 1,
color "base_color" default 0.8 0.1 0.0 1,
color "edge_color" default 0.0 0.0 0.0,
scalar "edge_color_bias" default 1.0,
color "lit_color" default 0.6 0.0 0.2,
scalar "lit_color_bias" default 8.0,
scalar "diffuse_weight" default 1.0,
scalar "diffuse_bias" default 1.5,
scalar "irradiance_weight" default 1.0,
color "spec" default 1 1 1 1,
scalar "spec_weight" default 0.2,
scalar "spec_exp" default 60.0,
color "spec_sec" default 1 1 1 1,
scalar "spec_sec_weight" default 0.3,
scalar "spec_sec_exp" default 25.0,
boolean "spec_glazing" default on,
color "flake_color" default 1.0 1.0 1.0 1,
scalar "flake_weight" default 1.0,
scalar "flake_reflect" default 0.0,
scalar "flake_exp" default 45.0,
scalar "flake_decay" default 0.0,
shader "flake_bump",
scalar "global_weight" default 1.0,
integer "mode" default 3,
array light "lights"
)
version 2
apply material
end declare
This shader is designed to create a bump map with the appearance of small individual flakes at slightly different orientations. It does so by slightly modifying the current normal vector based on a procedurally generated flake texture. It also returns a color that indicates the "intensity" for that flake.
declare shader "mi_bump_flakes" (
scalar "flake_density" default 0.5,
scalar "flake_strength" default 0.8,
scalar "flake_scale" default 0.2,
)
version 1
apply texture
end declare
Copyright (©) 1986-2008 by mental images GmbH